Today, Wuxi Rihuan Sensing Technology Co., Ltd. will introduce the core differences between photoelectric sensors and proximity sensors.
I. Working Principle
Photoelectric sensor: It has an internal emitter and receiver. The emitter emits modulated light, and the receiver detects the intensity/absence of changes in the light when it encounters an object, converting these changes into electrical signals for detection.
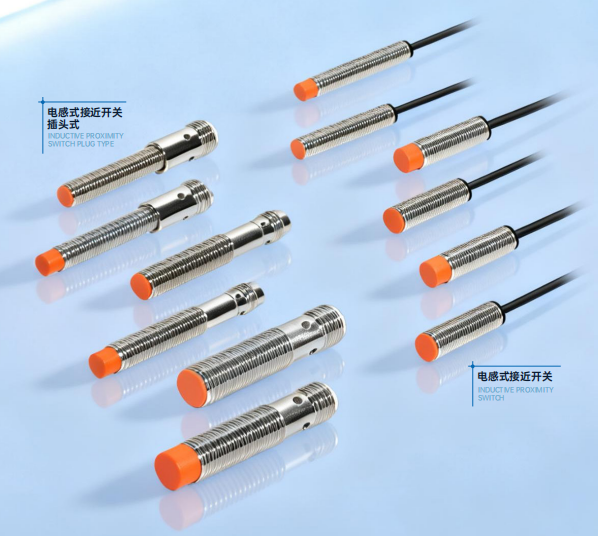
Proximity sensor: Without needing to touch the object, it generates a high-frequency magnetic field/electric field at the head to detect the eddy current effect (inductive type) or capacitance change (capacitive type) when the object approaches, thereby triggering the detection signal.

II. Core Features
Photoelectric Sensor: The greatest advantage is that there is no material restriction for detection, and it can accurately identify various objects such as metals, plastics, glasses, liquids, papers, powders, etc., and is suitable for multi-material mixed detection scenarios; the sensing distance can be flexibly adjusted, covering distances from a few centimeters to several tens of meters, which can meet different distance detection requirements; it should be noted that the sensing distance is directly related to the reflectivity of the object surface - objects with good reflectivity such as white and light colors have a longer sensing distance, while objects with strong absorption such as black and dark colors have a shorter sensing distance. Actual use requires adjusting the installation spacing according to the color of the object.
Proximity Sensor: According to the detected material, it is divided into two major categories. The inductive type is specifically suitable for metal object detection (such as steel, aluminum products, etc.), with strong detection stability; the capacitive type can be compatible with non-metal objects (plastics, papers, woods, liquids, etc.) and some metal material detection, and has a wider applicable scenarios. Both types of sensors focus on close-range detection, with a conventional detection distance of 0.1-10 centimeters, and the response speed can reach millisecond level, which can meet the requirements of high-speed detection, and at the same time has strong anti-electromagnetic interference and anti-dust interference capabilities, and is suitable for complex industrial environments.
III. Applicable Scenarios
Photoelectric Sensor: It is mainly applicable to long-distance detection, narrow-space operations, and scenarios where the measured object is prone to wear or cannot be closely contacted. For example, precise electronic component detection (such as chips, resistors) to avoid damage caused by contact; high-altitude material positioning (such as top materials of storage shelves), without the need to climb close to complete the detection; identification of transparent materials on assembly lines (such as glass bottles, plastic films), as well as material counting in harsh environments (such as workshops with a lot of dust) and other scenarios.
Proximity Sensor: It is mainly suitable for close-range, single-material precise detection in industrial scenarios, especially suitable for high-speed automated operations. Common applications include parts counting and positioning in automotive component assembly lines (such as bolt, gear detection), liquid level control of storage tanks in the chemical industry (either non-metal or metal storage tanks can be compatible with corresponding types), travel limit positioning for mechanical processing equipment (to avoid mechanical collisions), and non-contact button triggering (such as non-contact operation of industrial control cabinets) and other scenarios.
IV. Output and Selection
Output Type: Both types of sensors under Dayring Sensor support standard PNP and NPN output modes. They can be flexibly matched according to the interface type of the user's on-site PLC, controller, etc., without the need for additional conversion modules, reducing the complexity of equipment connection and improving installation and debugging efficiency.
Selection Principle: It is necessary to precisely match the detection requirements - if there is cross-material detection (multiple material mixed recognition), long-distance detection (over 10 centimeters), or facing special scenarios such as space limitation, easily damaged measured objects, transparent/dark object detection, etc., choose the photoelectric sensor first; if the detection environment is suitable for close-range operation (distance ≤ 10 centimeters), and is specifically for metal or non-metal single-material detection, and has higher requirements for response speed and anti-interference (such as high-speed assembly lines, strong electromagnetic interference workshops), then the proximity sensor is a more suitable choice.
V. Advantages of Dayring Sensor Products and Usage Notes
Product Optimization Advantages: For the complex requirements of industrial scenarios, Dayring Sensor has specially optimized the two types of sensors. The photoelectric sensor upgrades the anti-strong light interference design, even in outdoor strong light or workshop strong light sources, it can still stably receive light signals, avoiding false triggering; the proximity sensor optimizes detection accuracy and temperature resistance performance, the working temperature range covers -20℃ - 85℃, can adapt to cold storage, high-temperature workshops, etc., and at the same time improves detection repeatability, ensuring long-term stable operation.
